Which implants are used in a toothless jaw?
Complete tooth loss fix by permanently stuck dental implants look most natural. Especially after already occurred bone loss on the jaw, the treatment can be complex and a prior bone augmentation necessary. But the patience is worth it. In contrast to removable dentures, an implanted teeth in the mouth feels pleasantly natural.
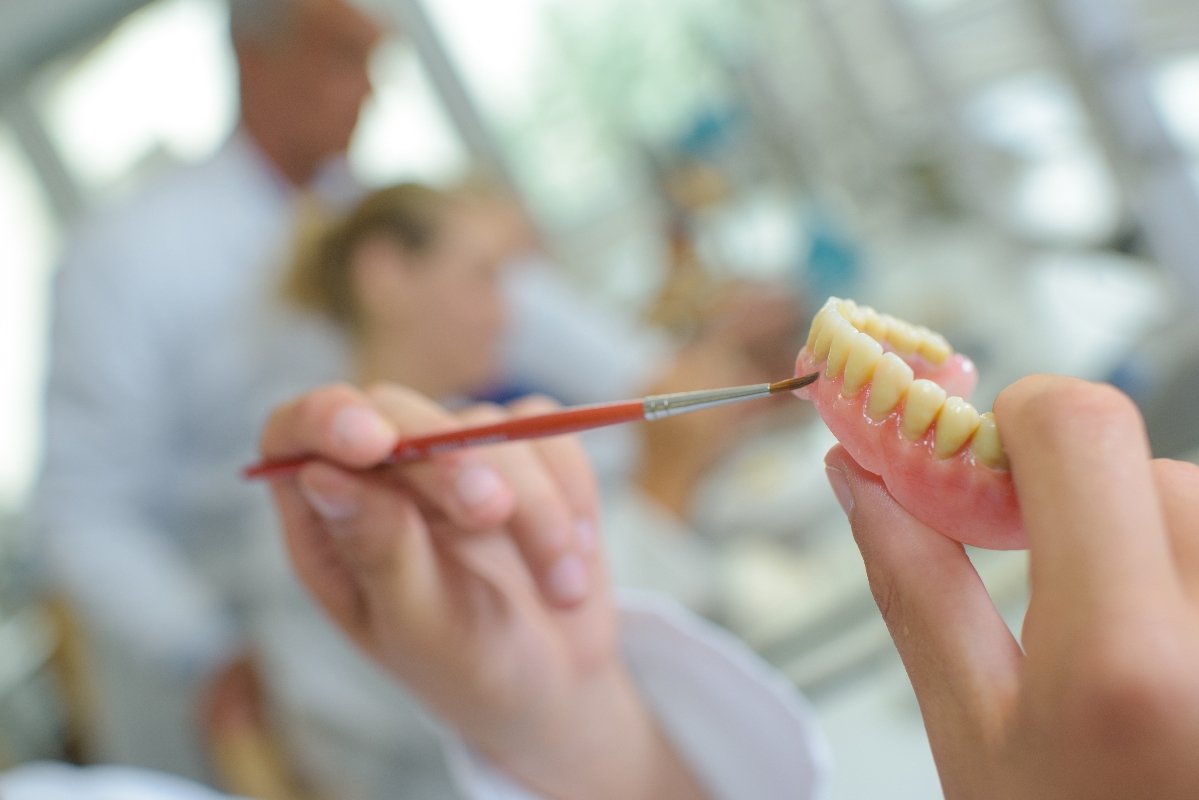
With complete tooth loss, the dentist does not put each tooth individually in the jaw. He uses the so-called all-on-4 or all-on-6 implants. The numbers indicate how many implant anchors each of the two jaws receive. In the case of the all-on-4 implant, there are two anchoring points per jaw side, and three for the all-on-6 implant. On the implants used in the jaw, the rows of teeth with the natural acting teeth are firmly mounted.
In dental terms, the term "implant" always refers to the part of the construction that is located in the jaw. The tooth crown sits on the implant. The total unit of implant and crown is colloquially usually referred to as an implant.
A prerequisite for the successful use of dental implants is a strong jawline. Prolonged edentulousness causes jawbone atrophy, a degradation of the bone substance of the jaw. The bone density decreases and thus the strength. The jaw is also narrowed by the continuous bone loss. These are not good conditions for long-lasting, permanent dentures. Here, the dentist rebuilds the jaw bone before he can use the implants safely some time later. Bone building of the jaw also takes place when someone naturally has very narrow jawbones or no dense bone structure.