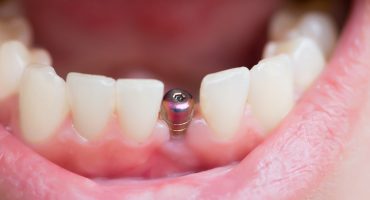
If there is not much left over from the anterior tooth than the tooth root, the dentist can create a new crown by using a pin anchored in the root. Such a pin tooth is significantly cheaper than a dental implant and receives at least a portion of the natural tooth. The procedure is similar to the insertion of an implant, which is why there is often confusion between these two variants of the dentures. Here you can find out what the differences are, how the pen structure works and what costs you have to expect.
What are pin teeth and what are they used for?
The colloquial term pin tooth stands for a pin-worn crown, often referred to as a jacket crown. Here, a pin is anchored in the tooth root and provided with an artificial tooth crown. This form of fixed dentures was already used in the 19th century. However, tooth and pin formed a unity at that time, from which the common name crown derives.
Today, pin teeth and crown are no longer connected. This allows the dentist to replace the crown if necessary without completely removing the pin. In addition, the pins can be used in modern models as a foundation for bridges and partial dentures. Therefore, the term "root canal-anchored building system" has become established among medical professionals.
A pin tooth is considered as a denture in question, if the tooth in question is not much substance or only the tooth root left. Often, dentists use it after a root canal treatment. It not only fills the unsightly tooth gap, but also ensures a mechanical stabilization of the tooth, which can thus be retained longer. This is only possible if the root is still completely, intact and sufficiently stable anchored in the jaw.
Tooth and dental implant - what are their differences?
Reason for the frequent confusion of these tooth replacement variants is the principle used in both "root - structure - crown". In contrast to the pin tooth, however, the dentist inserts the implant directly into the jaw as a replacement for the original tooth root. With pencil crowns, on the other hand, the natural root is preserved, even if the tooth is already dead. Due to their lower load capacity, pin teeth are used exclusively in the anterior region, while implants are possible throughout the jaw.
Dental implants last a lifetime, in principle. After ten years, the shelf life is about 90 percent. The life of the pen, however, is limited by the aging of the tooth root. If this natural holder no longer serves its purpose, the tooth must be completely removed and replaced with an implant or other dental prosthesis.
In contrast to the pin tooth, a dental implant must first fuse with the jaw before it is fully loadable. Therefore, the treatment takes much longer to apply the new crown than with a pin structure. Usually falls for a significantly higher costs.
How is the pin tooth used?
Since the tooth is often already severely damaged, the post construction in most cases begins with a root canal treatment. The dentist removes the pulp and ensures that the root canals are clean. Then he brings the pin, a so-called Radix anchor, into the tooth stump and fixes it with dental cement. The latter, after grinding, dries to give it a smooth surface.
For teeth with multiple root canals, the physician must first decide where to put the pin. As a rule, he uses an X-ray image to select the canal whose root best meets the following requirements:
- adequate anchoring in the bone,
- large diameter,
- correct insertion direction,
- straight course over a long distance.
If no channel meets all requirements, it may be necessary to insert several pins in the same tooth.
If the anchoring is firmly seated in the root canal, the dentist will equip the pin with a provisional crown. He then takes care of the surroundings of the tooth, especially the gumline. This offers on the one hand the tooth root with the pin tooth attached to it more stability and improves on the other hand also the aesthetics.
Regular follow-up checks ensure that the healing process is normal. If everything has healed well, the dentist replaces the provisional with a correct crown. As a material for this come ceramic, plastic or metal (titanium, gold or various non-precious metals) in question. The firm connection between the pin and the artificial tooth crown is created by a thread, adhesive or cement.
An alternative to normal construction is the indirect method. In the so-called cast post construction, the dentist first creates a jaw impression. On the basis of this impression, a dental laboratory prepares the dentures from the previously mentioned materials. He later anchors the finished tooth with a special cement in the tooth stump.
How much does a pin tooth cost and what does the health insurance pay?
The costs for a pin tooth depend essentially on the expense of the treatment and the material used. Pre-assembled pins are much cheaper than custom made pins. A pin crown made of ceramic is about twice as expensive as a plastic crown. You can roughly expect an amount of 500 to 1,000 euros. The health insurances take over from it only a diagnosis-oriented fixed subsidy in the context of the standard supply.
The assumption of full costs by the statutory funds is provided only in hardship cases. If you have a low income, you will receive a double (basic) fixed allowance. On average, the own contribution to be paid by health insurance patients is around 400 to 650 euros. Properly managing your bonus book over a five-year period will increase the fixed subsidy by 20 percent. If you have taken all the check-ups for ten years and had your bonus book stamped, the subsidy will increase again by ten percent.
If your dentist offers you an adhesive cementation of the pin tooth with plastic adhesives, this is a fee according to the fee regulations for dentists (FRD), which you must pay for out of pocket. The same applies if you opt for ceramic pins or carbon fiber posts for better compatibility and optics. The cash contribution relates exclusively to non-precious metals defined as balancing power.