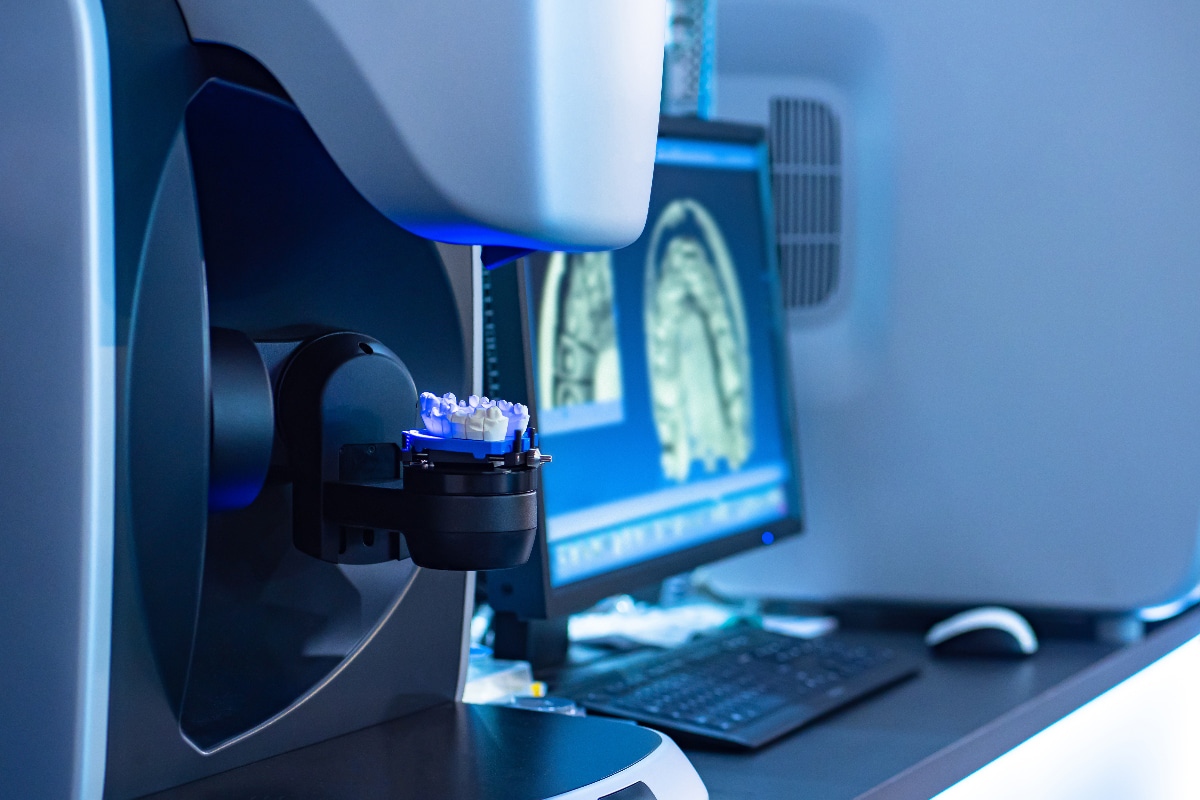
Dental volume tomography (DVT) is one of the most advanced methods of X-ray diagnostics. It is an imaging tomography method, in which 3D X-ray images are made. In this way, the examining doctor receives three-dimensional insights into the head structures with the utmost precision. As a result, he is able to examine the oral and jaw area three-dimensionally on all levels, recognizing the finest anatomical structures.
When is this X-ray technique preferred?
In Germany, dental volume tomography has its origins in dentistry. However, today's devices differ significantly from the older devices, also with regard to the radiation exposure. In the meantime, DVT is also being used under the name "digital volume tomography" in oral and maxillofacial surgery as well as in ear, nose and throat medicine.
One of the most important applications of dental volume tomography is the placement of implants in dentistry. For example, DVT is now regarded as indispensable in implant planning.
The method is extremely helpful in determining the position of displaced or supernumerary teeth. The use of dental volume tomography allows a precise planning of surgical interventions, allowing a gentle and minimally invasive surgery is possible.
In addition, the use of root canals in DVT makes root canal treatment extremely valuable.
What advantages does dental volume tomography offer to doctors and patients?
The basis of dental volume tomography was computed tomography (CT). Compared to this method, however, the DVT has up to 95 percent less radiation exposure. For dentists, 3D X-ray technology usually enables significantly more digestion than with conventional 2D technology. A shot takes just seven seconds. In addition, an x-ray video with 3D images can be produced in real time. The dentist looks at the impression as if he held the recorded jaw in his hand and could turn it as desired. The results of the DVT are evaluated immediately in the dental practice.
But even for the patients, the dental volume tomography is advantageous when they receive a dental implant. For example, DVT often allows an evaluation of the supply and quality of the bones. In this case, the placement of the implant can be simulated. But also for the exact treatment of a root canal, or the surgical removal of wisdom teeth, the dental volume tomography has its merits and allows a better quality treatment.
Indications
Typical applications of DVT include:
- diagnosis of diseased teeth and their preservation
- orientation of wisdom teeth and their influence on the facial nerves
- accurate positioning of dental implants
- planning an implant in a 3D simulation
- assessing the condition of the bone prior to insertion of an implant
- prospecting and assessing root canals during root canal treatment
- skeletal diagnosis in orthodontic examinations
- diagnosis of diseases of the maxillary sinus
- Representation of the periodontium in the context of periodontology
How does a dental volume tomography work?
The course of a dental volume tomography is similar to that of a conventional X-ray examination. The images are not held in a narrow tube, but can be compared with a 2D panoramic image. However, while in computed tomography several revolutions of the X-ray source, which revolves around the head of the patient are required, is sufficient for the DVT already a single orbit. All relevant image data are recorded. This process takes only a few seconds.
Are there risks for the patient during a DVT?
The risks associated with x-ray procedures include exposure to ionizing radiation. However, since the recording procedure in dental volume tomography is completed within a few seconds, the radiation exposure in this method is significantly lower.
Depending on local conditions, natural radiation exposure in Germany is between 2 and 5 mSv / a (millisievert per year). The average radiation exposure of a person is given as about 2.1 mSv / a. The natural cosmic radiation in Germany averages to 5.75 μSv per day. While the radiation load in a computerized tomography corresponds to approximately 788 + 334 μSv, in the case of dental volume tomography, it is only about 221 + 275 μSv, with which the DVT has significantly less radiation exposure.
Costs
The costs for a dental volume tomography are usually not covered by the statutory health insurance companies. Therefore, the patient has to pay the price of about 150 to 200 euros out of pocket.
CONCLUSION
Dental volume tomography offers both dentists and patients numerous advantages. It can be performed quickly and safely. However, patients usually bear the costs of the procedure themselves.
Weitere Beiträge
Distraction
Before an implant, i.e. firmly anchored dentures, can be used, there are preparatory measures for the intervention of the implantologist. Distraction osteogenesis or callus distraction is an operative procedure in the field of oral and maxillofacial surgery for new bone formation.