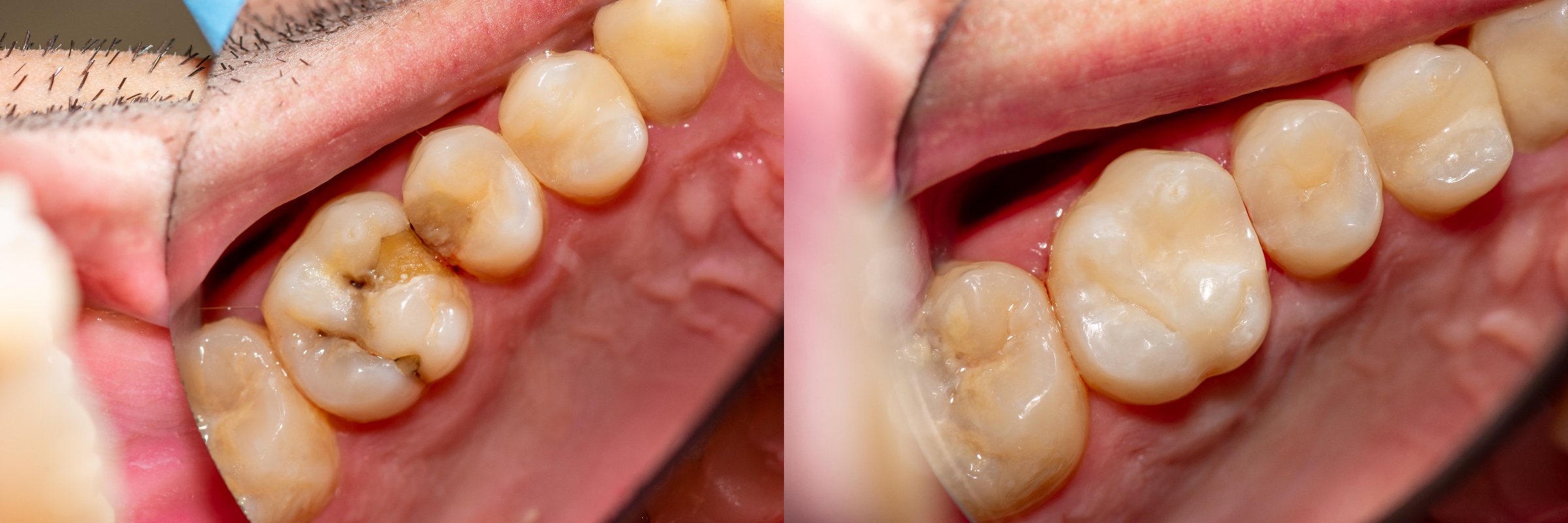
The main cause of the need for dental fillings is tooth decay. If the dentist removes them, there will be a gap in the tooth, which will be filled with it. With regard to the available materials, there are great differences, each with different advantages and disadvantages. How the dental fillings are suitable depends on the one hand on your personal wishes and on the other hand on the position of the tooth in the mouth. In addition, the extent of tooth damage also determines which tooth filling is used.
Types of dental fillings
The main difference between the different fillings is the degree of hardness. Soft materials include amalgam and plastic composite. Both serve to supply minor dental damage. The dentist makes it during your treatment and puts it directly into the tooth. They harden within a short time. Amalgam is now used less and less often because it is controversial of the mercury contained.
The hard fillings include ceramics or gold. They are also called insert fillings or inlays. They are used for larger findings. Your dentist will commission it externally in a laboratory. Often, a temporary restoration is performed to bridge the waiting time for the inlay.
The durability of the respective fillings is very different:
- composite lasts on average about five to ten years,
- amalgam about eight to ten years.
- a ceramic filling remains stable for up to 15 years,
- a gold inlay nearly 30 years.
More detailed information is not possible, since the shelf life depends essentially on the processing itself and your personal dental care.
Alternatives to dental fillings
Even if a conventional amalgam filling or composite for minor tooth damage are sufficient, there are reasonable alternatives.
An inlay closes every hole in the tooth in principle and has a much greater durability and stability compared to a simple filling. The reason for this is the individual and computer-controlled adaptation. The filling can be made so precisely that it has a much better fit with the existing gap. A ceramic solution can be applied throughout the mouth. However, unlike gold, it is mainly used for the visible teeth in the front and side area due to the optics.
Often, there is a desire to visually correct existing larger fillings or damaged incisors. Suitable for this purpose are so-called veneers, wafer-thin ceramic veneers, which are glued to the tooth. They are translucent and appear completely natural.
Need for dental fillings
In dentistry, a tooth filling is required if the outer tooth layer is damaged. This is possible both through a hole in the teeth and through a broken corner. As causes usually carries, a massive abrasion of the surface of the tooth or an accident in question. The sooner the damage is repaired, the better for the preservation of the tooth. If you wait too long, there is a risk of continuous tooth damage, including the loss of the tooth.
The respective dental fillings in turn offer advantages and disadvantages. With amalgam and composite, the advantage is the fast preparation by your dentist in practice. The lower costs speak for it. A disadvantage is the shorter durability and lower accuracy of fit compared to an inlay. For insert fillings, the exactness of the fit and longevity should be mentioned, but also the significantly higher price.
Course of a treatment
At the beginning of the dental treatment, the caries removed in the affected tooth, if necessary under local anesthesia. Then the tooth is cleaned. The further process depends on the material of the tooth filling.
Plastic fillers, such as amalgam or plastic, are mixed by your dentist and filled into the hole. Often an underfilling is used in advance. It serves to protect the tooth root.
In a composite filling, the dentist roughened the tooth surface slightly so that the filling sits better. An adhesive (base adhesive) is applied to the area, then layer by layer the filling material. Subsequently, a curing by a blue light lamp. Each filling is finally smoothed and polished using a grinder.
The inlay to be fabricated in the laboratory is attached to the tooth in a follow-up session with a special adhesive. The dentist uses ultrasound to anchor it in the exact position. The curing is done by a special UV lamp.
Costs and reimbursements
Dental fillings are very different in price. The cheapest material is amalgam. It is also the only one that is completely taken over by the statutory health insurance companies.
In a composite filling, it depends on the position of the tooth in the jaw. Only in the area of the anterior teeth or in case of proven allergy to amalgam will the costs be reimbursed. If both are not given, you are liable to pay. The fund takes over here only the portion that would be paid for amalgam. The amount to be paid depends on the size and extent of the deposit.
Ceramic fillings are among the most expensive materials. For this, the fund takes no cost, except for the amalgam share. Basically, a deposit filling applies as a denture at the health insurance.
The higher the material of the tooth filling, the higher the proportion of self-pay you normally pay. The exact prices are based on your specific findings and the respective effort for the material and the production. If a filling is planned, which is manufactured externally in a laboratory, the first step is the preparation of a treatment and cost plan. This is submitted to the health insurance for approval.
Conclusion
A tooth filling is required as soon as a tooth is damaged. Different materials are available for fillings. Soft materials (amalgam, plastic) are processed directly in the dental practice by your dentist. Hard materials (ceramics, gold) are made in a laboratory. They are based on accurate and computer-accurate calculations and are characterized by a longer shelf life. The statutory health insurance funds, depending on the material, only a part of the costs. Amalgam fillings are fully reimbursed.
Weitere Beiträge
CAMLOG-Implant
The company CAMLOG is one of the leading manufacturers in the field of implantology and produces dentures for the highest demands. In Wimsheim near Stuttgart, both complete systems and individual, implant-supported dental prosthesis products are manufactured.