The herpes-related oral blight
Cause of herpes-related oral blight is the virus of herpes simplex type 1 (HSC-1). In particular, in small children it may come at their initial infection with this herpes virus stomatitis aphthosa herpetic / gingivostomatitis herpetica. Occasionally, however, older children, adolescents and adults suffer from herpes-related mouth rot.
As early symptoms,
- fever,
- chills,
- headache and body aches and
- fatigue symptoms may occur.
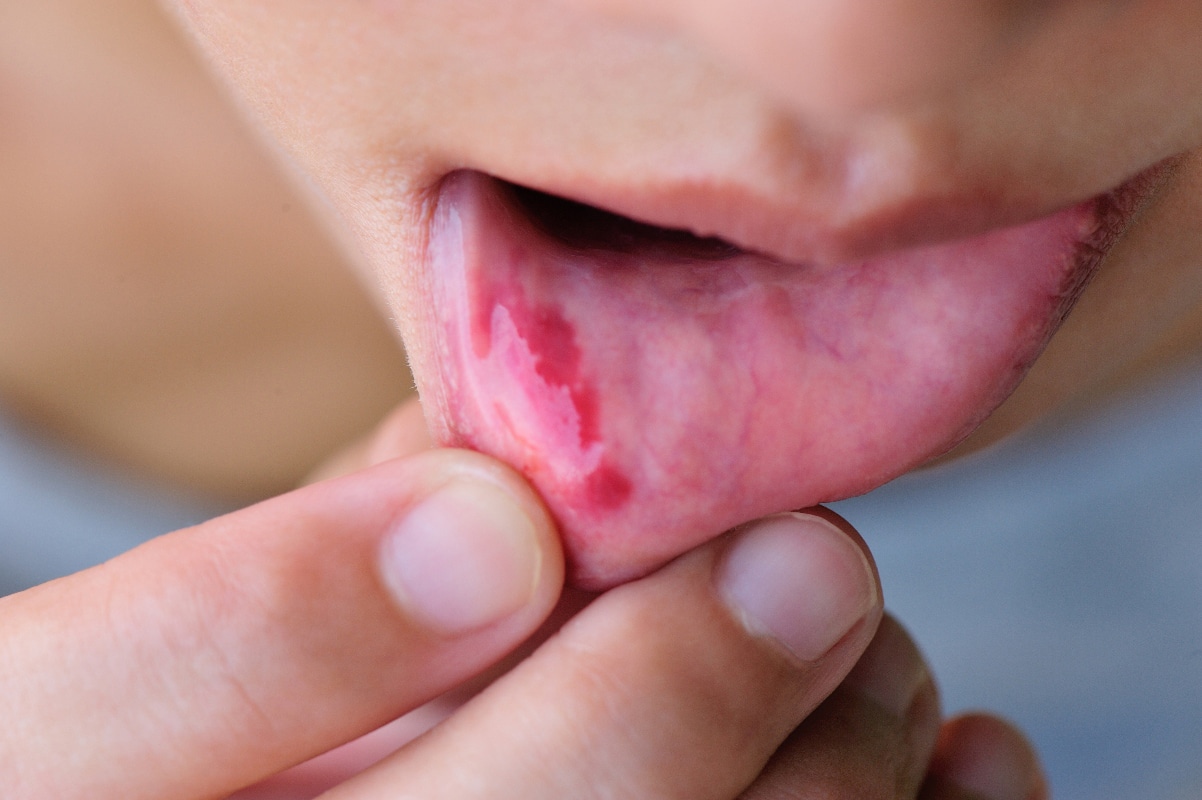
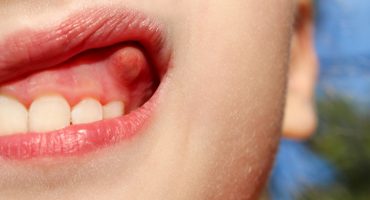
The actual herpes outbreak can affect a large part of the oral mucosa and therefore determines the symptoms. It comes to painful redness and herpes typical small blisters. They are filled with a clear or cloudy liquid; they burst and formopen aphids. The mouth rot is associated with bad breath. During the course of the disease, swelling of the lymph nodes may occur, which is normal in infections and indicates the activity of the immune system. In particular, when the virus spreads into the pharynx, dysphagia may occur. Attention: With the spread of the virus over the blood vessels in the entire body, the herpes sepsis, there is danger to life. If you suspect sepsis, do not hesitate to seek emergency medical help from a hospital.
For diagnosis, the oral cavity is examined; if necessary, a swab may be taken for an analysis procedure for the purpose of protection.
For infants, the oral blight is much more dangerous than for older children or adults. Infants and young children with stomatitis are in urgent need of medical care to get through the time of illness. It is also important to ensure that stomatitis does not lead to an undersupply of food and fluids. Chewing and swallowing can be temporarily associated with great pain, and some children refuse to eat completely. If complications do not occur, stomatitis heals aphthosa herpetica after the early symptoms, the following week with a pronounced symptom picture and a two- to three-week healing period.
Due to the risk of infection for others, the possible fever, the risk of sepsis and the pain of eating through pain, not only children but also adults should seek medical attention. The doctor may prescribe antipyretic and analgesic medications.