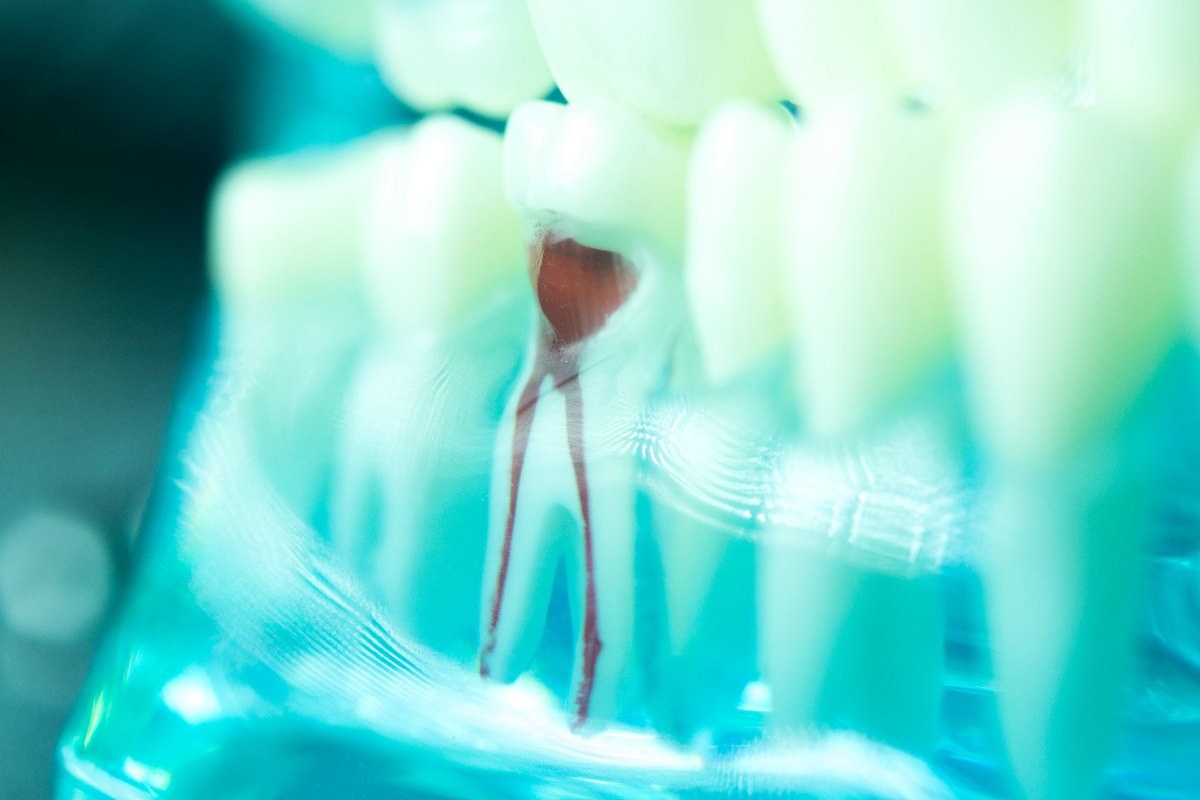
A dental root inflammation is a painful deep-seated inflammation within a tooth. The various names such as "root inflammation", or "tooth nerve inflammation" are often used in place of the correct term "pulp inflammation" (medical pulpitis). In this type of disease, the toothpaste located in the tooth cavity down to the tooth root has become inflamed.
What are the causes of tooth root inflammation?
Due to fine nerve tracts that run through the pulp, the term "pulp inflammation" was born. The word "dental root inflammation" results from the area in which the inflammation has developed - the tooth root. The same applies to the formulations "root canal inflammation" and root inflammation (apical periodontitis). In case of a timely intervention, damage to the dental pulp can be treated well. Anyone who waits too long with the visit to the dentist risks nerve damage and the death of the tooth.
In many cases, the occurrence of caries is the cause of inflammation of the tooth root. Without immediate treatment of the caries, the caries bacteria gradually penetrate through all tooth layers until they reach the pulp and ultimately the root tip.
- If Periodontitis(bacterial inflammation) has not been treated or is not completely treated, bacteria in the area of the gum can penetrate the tooth, attack the tooth root and ignite it.
- In more rare cases, a blow to the tooth or teeth grinding is the reason for inflammation in the tooth.
- Just as rarely, obliquely grown wisdom teeth are the trigger for an inflammation of the dental pulp.
What are the symptoms of tooth root inflammation?
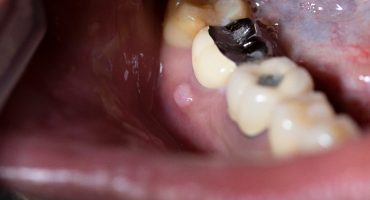
Inflammation of the most sensitive part of the tooth causes severe toothache. When eating, the already aching reacts tooth intolerably to pressure and heat and cold. Occasionally there is also an unpleasant throb. If the inflammation is not immediately treated by a dentist, it can also affect the jawbone and the surrounding tissue. As a result, an abscess develops, as well as a "thick cheek".
In addition, there is a risk of spreading the germs on adjacent teeth and their tooth roots, facial regions and in the body. If the affected tooth hurts and bumps hard and suddenly stops, then this is not a sign of spontaneous healing. Rather, the dental pulp and the inside are fine tooth nerves so severely damaged that the pain is no longer transmitted - the tooth is "dead".
The gums also suffer from tooth root inflammation. Brushing can cause bleeding. The Gums from back and expose the necks of the teeth, which react with pain. Occasionally, however, the gum pockets purge or liquid and lead to foul-smelling bad breath. Due to the damaged gums, the teeth lose their hold. In general, inflammatory processes in the body weaken the immune system and make it more susceptible to infectious diseases.
Here again are the Symptoms at a glance:
- severe toothache
- Pressure sensitivity when biting
- Pain on tapping (percussion pain)
- sensitive reaction to hot and cold food and drinks
- unpleasant throbbing in the tooth
- Thickening of the tooth root and arch on the jawbone
- Abscess on the gums
- Bleeding of the gums
- Regressing of the gums
- Bad smelling bad breath
- Teeth lose their hold
- Weakening of the Immune System
How is a tooth root inflammation treated?
With an injection, the doctor makes treating the area around the tooth painless. Preventively, the surface of the affected tooth is cleaned with ultrasound, curettes or scalers to remove concrements, tartar or plaques. Thereafter, the oral cavity is rinsed with antibacterial solutions so that no germs are trafficked during dental treatment. Now the actual root canal treatment begins. The dentist drills the tooth and removes the inflamed tooth. Tiny little instruments help him to clean the root canal. Then it is rinsed with antibacterial solutions, possibly cleaned again and rinsed again until the root canal is completely germ-free.
If the root canal was not infected with bacteria, it can be immediately closed again with a special root filling paste. If the root canal was bacterially infected, it will initially be provided with an anti-inflammatory and disinfecting filling- possibly even several times. Thereafter, an X-ray image is taken for control purposes to verify complete feeding. Because only a complete and dense filling guarantees that no bacteria can penetrate. Only now is the drilled hole in the tooth provisionally closed. If the tooth remains dry and odorless in the following days, it is supplied with the special root filling paste. Under certain circumstances, this will only happen in a second or third session.
What is a root tip resection?
In patients with a curved or very branched root canal, the process of cleaning is severely impaired. Therefore, the cessation of inflammation may take longer, become chronic or, in the worst case, persist in the root apex. The dentist will have to preserve the diseased tooth with a apicoectomy. It is a minor surgical procedure in which it cuts off part of the root tip and removes any inflamed tissue or cysts. After any surgery, infection, wound healing disorder or other injury may occur. For these reasons treatment with antibiotics should be considered as prophylaxis. If the pain persists despite all the measures described, the tooth must be pulled.
Implant and dentures after tooth loss due to tooth root inflammation
After tooth loss and complete healing of the inflammation and the wound in the jaw, an implant, a bridge or prosthesis, are the optimal solutions for closing the resulting gap in the dentition. They can replace the missing tooth aesthetically as well as functionally permanently. This treatment can be performed with a relatively short treatment time as a complete care. Confidently address one of our specialists on the costs.
Which preventive measures are there?
Since Caries Spreads slowly and is also the most common cause of inflammation of the teeth, annual check-ups at one of our dentists are the first good option for prophylaxis. The second very sensible measure is adequate oral and dental hygiene. This means that you can thoroughly clean your teeth at least once in the morning and once in the evening. This includes cleaning the teeth from behind, not forgetting the back teeth, and cleaning the gums and tongue. For the hygiene of the interdental spaces brushes, dental floss or small interdental should be used at least once a day. Toothbrushes are consumables that should be renewed after about two to three months. Of course, this also applies to the attachments of electric toothbrushes.
If Sensitivity to cold and hot foods occur, it is best to make an appointment with the dentist immediately.
Weitere Beiträge

Dental Accident
Dental accidents happen more often than you might think: especially during leisure time and during sporting activities, it can very quickly lead to tooth injury. All age groups are affected in principle - children, adolescents and active athletes, however, in particular.