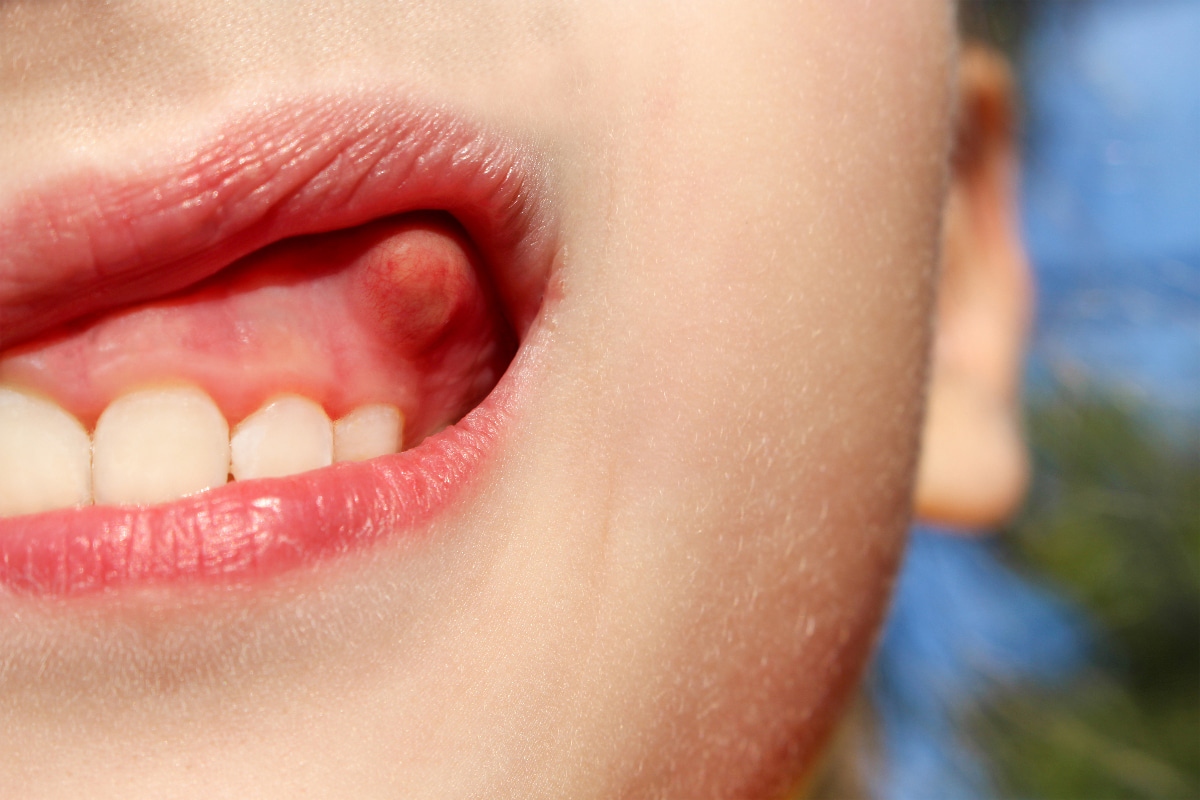
Can an abscess on the tooth become dangerous?
If there is any suspicion that the change in the gum may be an
abscess, the affected person should immediately consult a dentist. Even
if existing uncertainty applies: it is better to be safe than sorry and
go to the doctor. A tooth abscess is by no means a joke. It can even
become life threatening.
An untreated tooth abscess will gradually increase. It displaces
further body tissue, which also means its destruction. The tissue damage
can persist permanently despite successful treatment of the abscess.
Even the tooth triggering the abscess often suffers damage from the
infection and can die off. In addition, the infectious action of the pus
corpuscles of dentures is not just limited to the gums. The infection
can destroy the tooth. It can spread to the jawbone and continue there
as a jaw abscess.
The dangerous consequences of a non-treated or late-onset dental
abscess is not just limited to the oral cavity. This can lead to dreaded
infectious cellulitis . By the way, it has nothing to do with the
cellulite of the skin surface, which is often discussed aesthetically.
Rather, infectious cellulitis is an infection of the skin and
subcutaneous tissue usually caused by streptococci or staphylococci.
Such dermatitis easily becomes the gateway for bacteria to other areas
of the body where they cause further damage, even to vital organs.
Possible dangerous consequences here are liver dysfunction, kidney
failure, lymph node inflammation, meningitis, respiratory and
circulatory disorders and sepsis.