Die Kieferchirurgie ist ein Fachbereich der Zahnmedizin. Sie wird auch als Mund-Kiefer-Gesichtschirurgie bzw. kranio-maxillo-faziale Chirurgie bezeichnet.
Definition: Maxillofacial surgery
It includes the diagnosis, prevention, therapy and rehabilitation of diseases, fractures, injuries and malformations of the jaw, teeth, periodontium, oral cavity, covering soft tissues, face and facial skull. As a predominantly surgical discipline, she specifically covers all surgical procedures in the area of the face, oral cavity and jaw, which serve the functional (swallowing, chewing, speaking) and esthetic care of the patient.
Oral Surgeons / Specialist in maxillofacial surgery
A maxillofacial surgeon is a specialist in oral and maxillofacial surgery (MKG surgery). The oral cavity, face and jaw are highly complex areas of the human body and require a comprehensive understanding and a holistic, professional specialization. For this reason, a maxillofacial surgeon must have completed both a degree in human and dental medicine as well as a five-year further education in a specialist clinic or a specialist in private practice.
In the run-up to the medical exam at the Medical Association, a prospective oral surgeon must be able to demonstrate a comprehensive catalog of operations with oral surgery as well as trauma, tumor surgery and plastic surgery. In addition, oral surgeons can specialize in the field of plastic-reconstructive surgery of the head and neck as part of a three-year additional training.
Services / treatment spectrum of maxillofacial surgery
The extensive treatment spectrum of an oral surgeon includes all functional and / or aesthetic impairments in the area of the face, teeth, oral cavity and jaw. In detail, these include:
Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory infectious diseases, functional disorders and pain syndromes
- from the dental system outgoing inflammatory diseases
- Pain syndromes and functional impairments in the temporomandibular joint
- dental system Outbreaks of gland disorders Respiratory impaired sleep
- Disorders of the jaw and facial nerves
- Microsurgical restoration of nerve functions
Dentoalveolar Surgery
- Resection (removal) of fractured (dislocated) or dislocated (displaced) teeth and tooth, for example,tooth
- resection Root tip resection
- germs whitening Cyst treatment repair of prosthetic bearings bearing Maxillary reconstruction of
- Periodontal surgery
- Surgical(dental prostheses sit on a so-called prosthetic)
Dental implantology Dental
- implants
- atrophy or disintegration of the jawbone
- Displacement of tissue correction of malformations
- Nerve Surgical treatment lung of cleft lip and palate
- operative treatment of malformations of the skull development
- vocal tract improving surgery
- surgical treatment of Kieferfehlstellungen such as a Progenie (of the lower jaw by disproportion between the upper and lower jaw) accident surgery and plastic reconstructive surgery
- surgical treatment of soft tissue injuries and facial fractures
- plastic- Restoration surgery of bone and soft tissue defects
- Cosmetic treatment of accidental scars and aesthetic corrections after tumor treatment
- Surgical treatment of all tumors (benign and malignant)the face as well as functional and cosmetic-aesthetic restoration
- Laser therapy
- around Non-operative therapeutic approaches and supportive therapy for malignant tumors
- Diagnosis of systemic diseases, precancerous conditions (tumor precursors) and tumors in the oral cavity, the Facial skin and the facial skull
Diagnosis in maxillofacial surgery
Oral surgery must be planned carefully. Therefore, not only traditional X-ray procedures are used for treatment planning, but also modern 3D technologies. Imaging techniques such as computed tomography or digital volume tomography allow a precise representation of the anatomical structures in the area to be operated and thus ensure the optimal choice of surgical strategy. In addition, the individual operation steps can be simulated and the oral surgeon can visualize the surgical result for the patient before the procedure.
Computed Tomography
In particular, the diagnostics and surgical planning of more complex tasks are planned with three-dimensional imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT). Computed tomography allows high-resolution images of the head, which reproduce the relevant details in the area of the jaw to be treated three-dimensionally and metric accurately. In addition, it allows a differentiated representation of hard and soft tissue. A computed tomography is used in the oral surgery especially for the presentation and assessment of
- abnormal changes such as malignant tumors or cysts,
- malpositions of teeth and their adjacent structures,
- bony changes,
- diseases of the antrum,
- diseases of the temporomandibular joint,
- diseases of the salivary glands,
- inflammatory changes and soft tissue abscesses.
In addition to implantological planning, computed tomography is also used for follow-up and complications diagnostics.
Dental volume tomography
A dental volume tomography (DVT)is mainly used for 3D visualization of hard tissue in the field of oral and maxillofacial used. It is used in traumatology and dental implantology and serves primarily
- the foreign body localization of
- the representation of temporomandibular joint diseases as well as of bony tumors as well as
- bony changes in Kiefer Spaltbildungen as well as shape and position anomalies.
Weitere Beiträge
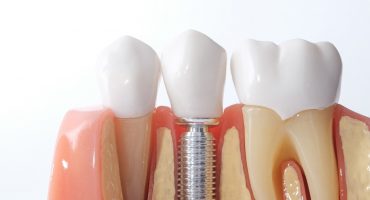
Implantology
Tooth loss can affect patients of all ages. Triggers may be, for example, accidents, tooth decay, periodontitis and tumors. The loss of teeth usually leads to severe limitations in the affected person in terms of functionality and appearance. Modern implantology provides a wide range of individual options for reliably eliminating the limitations and restoring functionality and aesthetics.