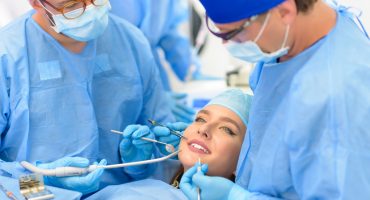
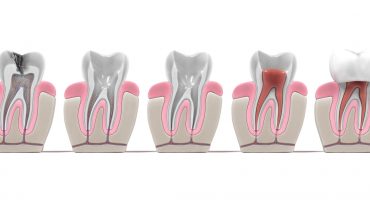
Aesthetic dentistry is a scientific discipline whose main task is to carry out dental restorative measures in accordance with aesthetic principles. It builds on all other areas of dentistry and adds to the holistic view of facial harmony. Latest materials and technologies help to restore the natural appearance of the teeth and their function in the best possible way.
Specialists in Aesthetic Dentistry
Dentists and dental technicians who want to identify aesthetic dentistry as a focus of their practice require special training. This has been offered since 2001 by the DGÄZ (German Society for Aesthetic Dentistry eV), which upon successful completion of the qualification certificate "Specialist in Aesthetics and Function in Dentistry / Dental Technology of the DGÄZ" awards.
A dentist who wants to be trained as a specialist must have at least five years of professional experience and sixteen training courses (= 256 training hours). The theoretical basis is also the "DGÄZ-APW-Curriculum Aesthetic Dentistry". The training itself includes the following topics:
For Dentists:
- Aesthetics
- Aesthetic Planning and Therapy
- Function and Total Rehabilitation Concepts
- Periodontics, Implantology, Endodontics
- Composite, Ceramics, Crowns & Bridges
- Partial Prosthetics, Hybrid Prosthetics, Total Prosthetics
For Dental Technicians:
- Aesthetic Basics
- Planning Concepts,Function
- CAD / CAM
- Implantology
- Ceramics, Crowns & Bridges
- Partial Prosthetics, Hybrid Prosthetics, Total
Prosthetics Aesthetic Dentistry Areas
People who naturally have beautiful teeth can count themselves lucky. Through Consistently operated oral hygiene, they can themselves help ensure that their teeth keep their youthful freshness until old age. In the best case, the support provided by Aesthetic Dentistry is only a regular Professional Dental Cleaning (PZR) as a prophylactic measure. Aesthetic Dentistry is where where
- discolored or damaged teeth,
- misaligned teeth,
- dental defects or
- inflamed gums
Disturb the overall picture, or even give the impression of neglect. In doing so, she does focus not on idealized role models, but on nature. With fillings, inlays, veneers, crowns or dentures, a specialist in dental aesthetics will always try to include discrete, irregular, irregularities in the patient's teeth, rather than putting their teeth unnaturally together like piano keys.
Treatment spectrum of Aesthetic Dentistry
Aesthetic Dentistry offers a variety of methods for optimizing the aesthetics of the teeth, which also have a positive effect on oral health. For example, the orthodontic shaping of the dental arches facilitates the care of the teeth, while restorations such as fillings and crowns are required for tooth preservation. The Most common methods of aesthetic dentistry include
- Veneers: Veneers are very thin ceramic veneers, which are used primarily in the anterior region. Modern veneer techniques make it possible to gently correct teeth. In direct veneering with composites often even the grinding of the teeth is eliminated.
- Inlays: Inlays are small, precisely fitting workpieces made of gold, ceramic or plastic, which when glued into the tooth, serve to restore caries and wear-damaged posterior teeth, especially their chewing surfaces.
- Crowns and bridges: With crowns and bridges, destroyed and missing teeth can be invisibly replaced. Made exactly to measure in a dental laboratory, this dental prosthesis ensures a completely natural dental sensation with optimal function at the same time.
- Implants: Implants provide the ability to close gaps in the teeth without damaging adjacent teeth. Instead of the natural tooth root set in the jawbone, they grow firmly into the tissue and thus form a stable foundation for dental crowns, bridges of complete dentures.
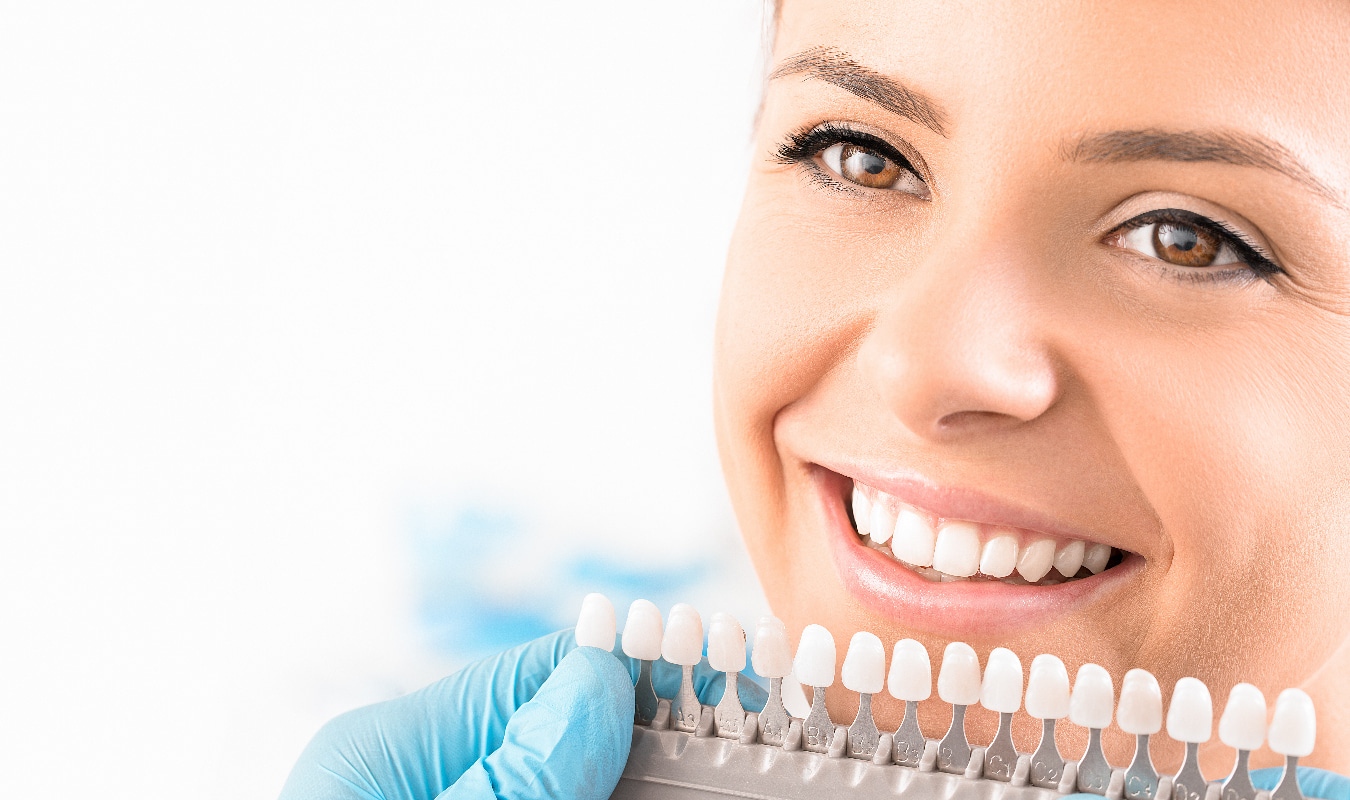
- Bleaching: The various bleaching procedures are used to lighten individual teeth or whole rows of teeth for aesthetic or cosmetic reasons. Which method is used depends on the cause of the discoloration and its extent.
Orthodontics:orthodontic Modern methods and devices can be used to correct even complicated dental malocclusions. Straight tooth placement not only improves teeth functions such as chewing and talking, but is also often the prerequisite for optimally designed dentures.
What are the costs and what does the health insurance pay?
The cost of a dental restoration depends essentially on the technology and the materials used. For example, small tooth-colored fillings start at a surcharge of 35 euros, while a tooth completely coated with highly esthetic ceramics can cost up to almost 1,000 euros.
Whether the statutory health insurance funds the private reimburser take part in the expenses for the treatment depends on whether it is a purely cosmetic procedure or whether there is a medical indication. If the latter is the case, the costs will be at least partially reimbursed depending on the insurance, the contract and the findings.
Weitere Beiträge
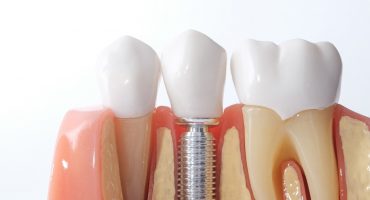
Implantology
Tooth loss can affect patients of all ages. Triggers may be, for example, accidents, tooth decay, periodontitis and tumors. The loss of teeth usually leads to severe limitations in the affected person in terms of functionality and appearance. Modern implantology provides a wide range of individual options for reliably eliminating the limitations and restoring functionality and aesthetics.