A root tip resection is far more harmless than the name suggests. It is a proven dental procedure that not only serves to preserve teeth, but also prevents infections from spreading further. Interesting information about the topic root tip resection can be found here.
What is a root tip resection?
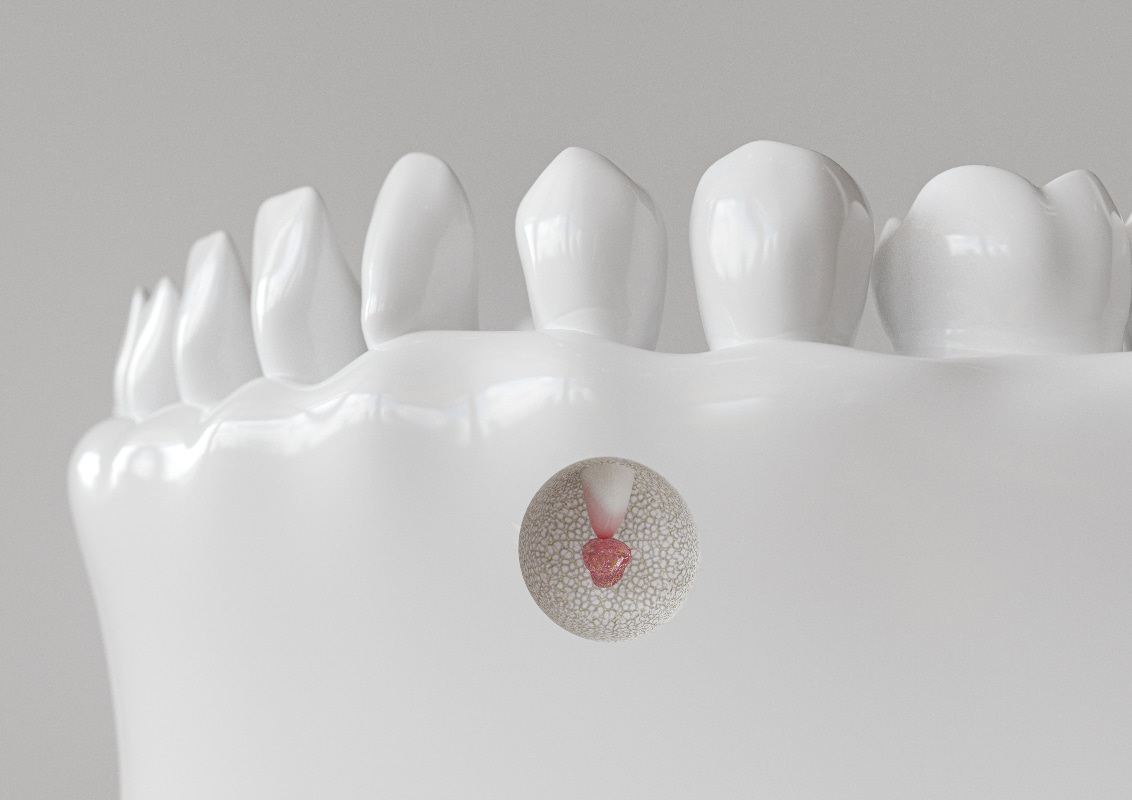
In the course of a root tip resection the tooth root tip of a diseased tooth is resected, thus removed. Root tip resection is also suitable for removing a cyst in the area of the tooth root. However, the procedure should not be confused with the root resection, in which the dentist separates the entire tooth root. Provided the root tip resection is successful, the tooth will be permanently preserved despite caries and / or infections. The root tip resection is therefore often the last alternative before pulling a diseased tooth.
When is a root tip resection necessary?
The root tip resection is carried out especially when caries has already led to inflammation in the tooth interior. In this case, there is an expansion of the blood vessels, which can press on the nerve and cause severe pain. In addition, there is a risk that bacteria spread to the root of the tooth and from here on over bones or nerves in the face. Even a spread of bacteria throughout the body is possible in the worst case.
To save the tooth, the dentist usually performs a root canal treatment first. Only then, if this is unsuccessful, follows the root tip resection. In many cases, a root canal treatment is not even possible - for example, because the root is too curved. Here is an overview of other possible reasons for performing an root tip resection:
- Broken tooth root
- Fracture at the root tip
- Infection after root canal treatment
How does the procedure work?
The root tip resection is usually performed by an oral surgeon. Depending on the individual clinical picture, anti-inflammatory drugs or even antibiotics are prescribed a few days before the procedure. Immediately before the root tip resection, an X-ray image is taken.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia and only in very rare cases under general anesthesia. Pain is therefore not to be feared - most patients only feel some pressure in the affected area. Once the local anesthetic has been fully effective, the oral surgeon cuts through the gums and periosteum of the tooth. Then he folds the tissue over so that he gets a clear view of just that part of the jawbone under which the root apex is located.
If necessary, the doctor will remove the jaw bone with a laser or a bur until the root of tooth becomes visible. This is then shortened by about two to three millimeters. Inflammatory tissue can also be removed by the doctor on this occasion. After disinfection, the surgeon inserts a special filling into the root canal, which seals the tooth. Finally, the tissue is folded back and the wound is carefully sutured before another X-ray image is taken for control.
A particularly precise method of root tip removal is microsurgical root tip resection. Here a special microscope is used, which allows the doctor to work absolutely accurately. However, the costs for a microsurgical root tip resection are not covered by the health insurance companies.
How long does a root tip resection take?
The duration of root tip resection depends on several factors, including the difficulty of the procedure and the location of the tooth. Thus, the view in a molar tooth is usually very limited, while the doctor usually has a good insight into the affected area in a root tip resection on a front or an incisor. The average duration of a root tip resection is about 60 minutes.
The root tip resection was not successful - what now?
If the symptoms of an infection disappeared immediately after the procedure, chances are very good that the root tip resection has led to the desired success and the tooth can be preserved. After three months, X-rays are used to check whether the jawbone heals well. Another six to nine months later, the doctor will take another X-ray to make sure that there are no more sources of inflammation.
If pain occurs again, the tooth usually needs to be removed. Only in rare cases, the root tip resection is performed a second time.
What are the risks and complications of a root tip resection?
As with any surgical procedure, it can also lead to bleeding and infection in the root tip resection. Also, damage to nerves, muscles, bones or to surrounding teeth are possible. In some people, the root tip resection causes irritation of the nerves in the lower jaw, which is associated with a temporary numbness and taste disorders. Severe complications are very rare in a root tip resection.
Post-OP Behavior Tips
After root tip resection, you should not eat anything until the effect of anesthesia has completely diminished. Even then, you should eat soft foods that do not require intense chewing. It is also advisable not to drive, smoke or drink for at least 24 hours. Also sports, saunas and tanning sessions should be avoided for about a week. However, a sick leave is usually not required - unless you perform a physically demanding job.
Pain and swelling after root tip resection can be alleviated by cooling. In addition, the doctors usually prescribe a painkiller. Important: Do not take painkillers other than those prescribed by your doctor, as some drugs increase the tendency to bleed. The threads are removed after seven to ten days.
Conclusion
Not every seriously ill tooth has to be pulled. Instead, root tip resection is a reliable way to maintain a carious or infective tooth in the long term. The procedure is considered very safe and has already saved many patients from artificial dentures.
Weitere Beiträge
Navigated Implantology
Digital imaging techniques are becoming increasingly important in dentistry. They allow precisely manufactured, perfectly fitting dentures and facilitate the work of the process involved easier. An enormous benefit for patients is the predictability of the treatment.