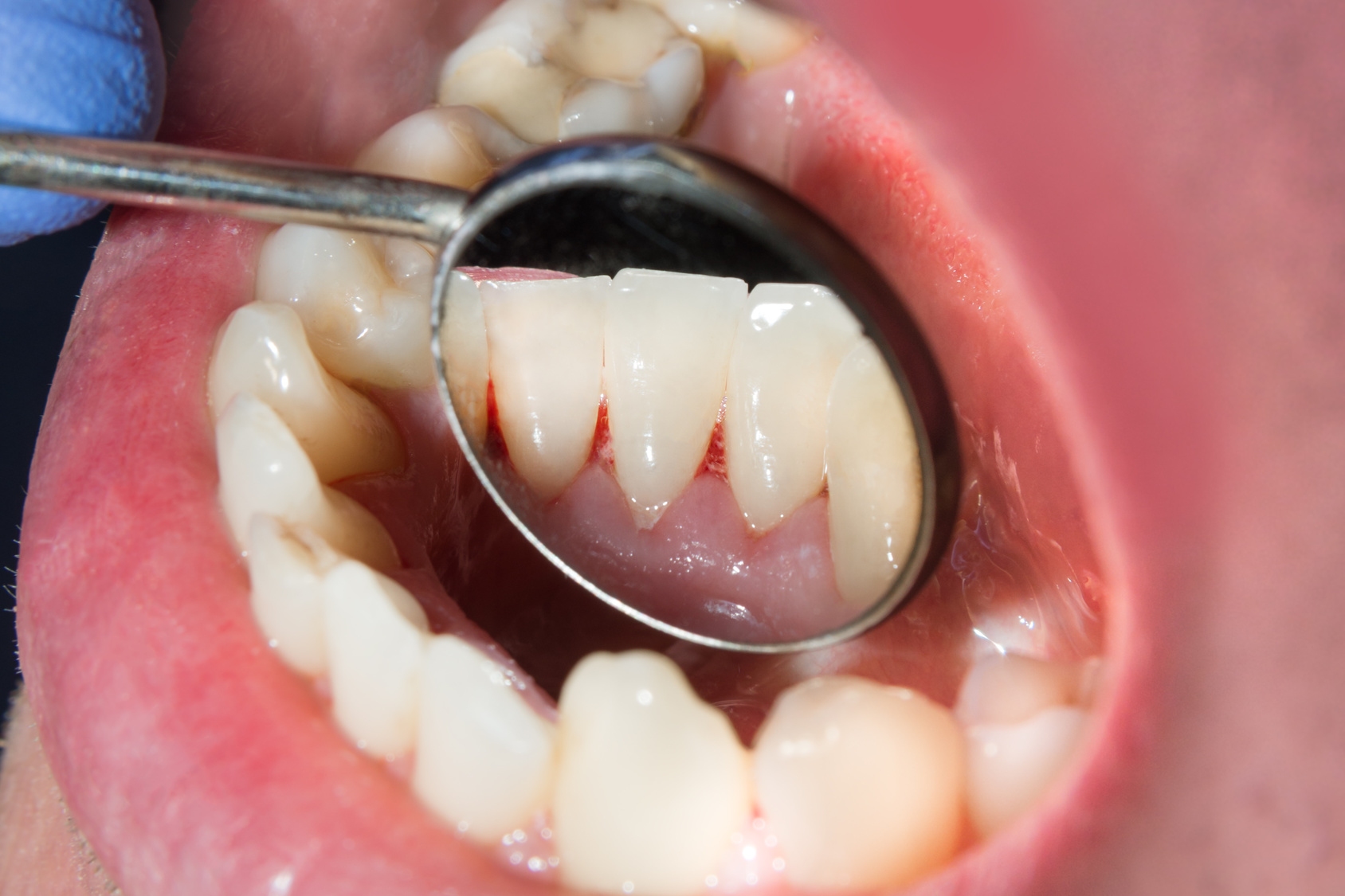
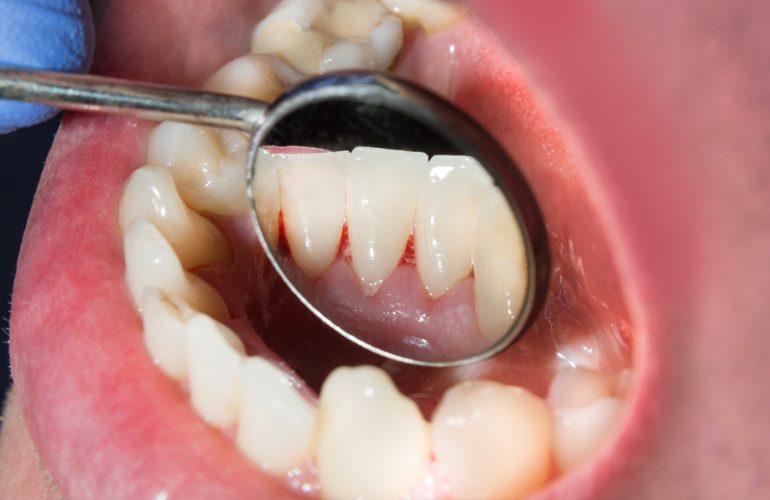
Plaque is a whitish coating of bacteria and sugar on the teeth. It forms continuously on the teeth and must be removed accordingly regularly, as it is the main cause of tooth decay and gum disease. Through daily, thorough oral hygiene, the plaque is easy to remove and severe complications can be stopped.
What is plaque?
Plaque consists of several complex layers containing proteins, carbohydrates, phosphates and microorganisms. The plaque stands especially where the tooth surface can not be kept free of coating by targeted cleaning. You can often not see plaque, but feel very well. Slipping the tongue over your teeth makes them feel rough, dull and uneven when covered with plaque. Incidentally, plaque should not be confused with nicotine, tea or coffee yellowish teeth. These discolorations are cosmetic in nature and, unlike plaque, are not dangerous to the teeth.
Causes of plaque
Plaque develops involuntarily in every human, because the mouth is constantly colonized with a variety of bacteria. These bacteria feed on components of our food and saliva. First of all, on all tooth surfaces (also fillings, crowns and artificial dentures) a harmless coating of saliva protein is formed, which is easy to rinse off. This protein layer is a good breeding ground for all bacteria that are present in the normal oral flora. If this plaque is not removed regularly, the colonization of bacteria on the protein layer is undisturbed. They multiply unchecked in an unhealthy for the oral flora. Between the bacteria, a network of protein and carbohydrates is created, which serves both as a food reserve for the bacteria and as a layer for mechanical reinforcement of the plaque. As a result, the plaque is firmer and the formation of tartar threatens.
In high and frequent sugar consumption, the propagation of microorganisms in the plaque is also favored. Existing plaque already forms a good breeding ground for these microorganisms. By constantly feeding sugary foods and drinks, they get exactly the foods they need for uncontrolled reproduction. In the conversion of sugar but these microorganisms from by-products, which involuntarily lead to an increase in the acidity in the saliva. The enamel is attacked directly and the formation of tooth decay is the result. In addition, some of these microorganisms constitute substances that reduce the body's immune defense and thereby cause inflammation in the oral cavity, such as the oral cavity. Cause gingivitis and periodontitis.
How can plaque be visualized?
Plaque on the teeth is invisible and does not hurt. Therefore, the detection of dental plaque with the naked eye is usually not possible. To make it visible, special staining tablets or solutions are used. Through a chemical reaction of the active ingredients in the staining solutions and the microorganisms that make up plaque, the teeth discolor exactly where plaque is present, i. in the places where the teeth have not been sufficiently cleaned. Nowadays, especially the two-color staining method is used. Here, old and new plaque can be differentiated in color and accordingly better conclusions about the cleaning method and cleaning effect of oral care products are given. Older plaque appears blue, later plaque is pink. By simply brushing your teeth, these stains can be easily removed. In children as well as adults, this type of plaque staining on teeth can be safely applied daily and over a longer period of time to check the thoroughness of dental care and to correct any wrong brushing behavior.
The monochromatic staining method is only used in rare cases. The erythrosin tablets used for blue staining of the teeth are highly iodine-containing, which is not tolerated by all patients and especially not over a longer period of time. Furthermore, erythrosin is also suspected to cause allergies, although it is approved as a food. Especially in recent times, the drug is also very controversial because of suspected side effects. If you need staining tablets to control your tooth brushing behavior, please make sure not to buy erythrosin-containing tablets in retail stores, as these are still occasionally offered.
In dental practices, the staining of the teeth is more likely to be due to a fluorescein-added rinse solution. Under UV light the plaque fluoresces, in normal light the staining remains invisible. Just this property makes this type of staining for the dentist interesting because the teeth do not need to be cleaned before further treatment. Health risks are not to be expected exactly as in the two-color staining.

Prevention is the best treatment
The effective protection against plaque is a careful and intensive oral hygiene. At least twice brushing your teeth should be the order of the day. In no case should one forget the interdental spaces, because here lurks most of the plaque due to the heavy access with the toothbrush. Plaque can only be completely removed by a combined use of toothbrush and floss, with which you can then clean both the tooth surface and the interdental spaces. The proper use of dental floss should be shown by a dentist, because not only can the cleaning be insufficient, but also the sensitive gums can be irritated and damaged.
Another preventive measure is to pay attention to the right diet. You do not have to give up sweets completely, but they should be as rare as possible on the menu. It makes sense not to nibble unchecked throughout the day, but to have a good snack once a day and then brush your teeth thoroughly. In addition to sweets, one should not resort too often to sweetened lemonades and very sugary fruit juices. Especially with small children, special care should be taken not to fill in the bottle sugary sodas, juices or teas to avoid harmful plaque on the particularly sensitive deciduous teeth.
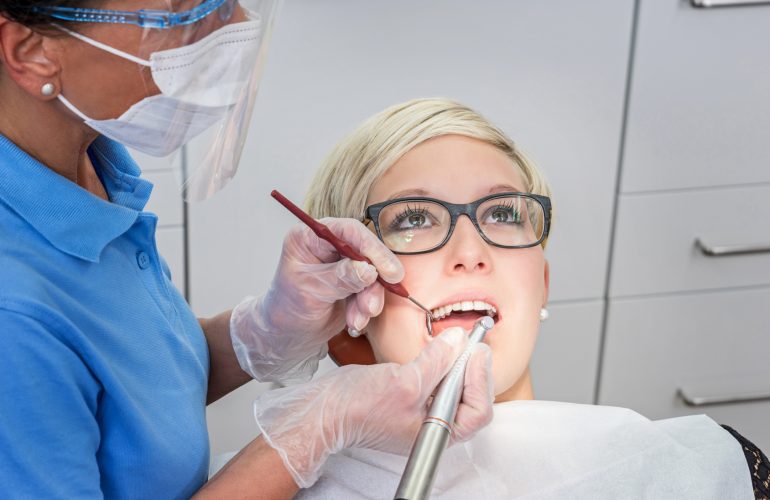
Professional dentistry (PTC) against plaque
At least twice a year, professional teeth cleaning (PTC) should also be performed to prevent gingivitis and periodontitis by thoroughly removing plaque and tartar. A PTC costs depending on the dentist and extent of cleaning between 50 and 150 euros and is unfortunately not covered by the general health insurance. It should be understood, however, that not all incurred treatment costs for the possible serious consequences of inadequate oral hygiene (such as tooth decay, gingivitis or periodontal disease) will be covered by the health insurance. The costs incurred here can exceed the cost of a simple PTC many times over. The right precaution in this case is cheaper than the aftercare.
If you have an additional dental insurance, then a part, in some insurance, even the entire cost of a PTC. Just ask your insurance company about the extent to which costs and how often per calendar year are covered. Since such supplemental insurance per month is not very much cost, it often makes sense not to pay the PTC in private, but instead to take out additional insurance that fully covers the costs. She will then pay for other dental treatments that are not paid by the general health insurance.